When a rightward force is applied to a dresser, a captivating dance of forces unfolds, revealing the intricate relationship between motion, equilibrium, and the dresser’s destiny. This exploration delves into the fundamental concepts of force and its profound impact on the dresser’s stability and trajectory.
As we unravel the dynamics at play, we uncover the types of forces that can act upon the dresser, their characteristics, and their everyday applications. The concept of equilibrium emerges as a delicate balance, where opposing forces cancel each other out, maintaining the dresser’s stillness.
We delve into the conditions necessary for equilibrium and explore real-world examples of objects gracefully suspended in this state.
Force and Motion: A Rightward Force Is Applied To A Dresser
Force is a physical quantity that describes an interaction that changes or tends to change the motion of an object. Force can cause an object to accelerate, decelerate, or change direction. Force is a vector quantity, which means it has both magnitude and direction.
There are many different types of forces, including gravitational force, friction, tension, and normal force. Gravitational force is the force of attraction between two objects with mass. Friction is the force that opposes the motion of an object when it is in contact with another object.
Tension is the force that is transmitted through a string or cable when it is pulled. Normal force is the force that is exerted by a surface on an object that is in contact with it.
The relationship between force, mass, and acceleration is described by Newton’s second law of motion. Newton’s second law states that the acceleration of an object is directly proportional to the net force acting on the object and inversely proportional to the mass of the object.
Types of Forces
There are many different types of forces, including:
- Gravitational forceis the force of attraction between two objects with mass. The greater the mass of an object, the greater its gravitational force.
- Frictionis the force that opposes the motion of an object when it is in contact with another object. The greater the surface area of contact between two objects, the greater the friction.
- Tensionis the force that is transmitted through a string or cable when it is pulled. The greater the tension in a string or cable, the greater the force that is exerted on the objects that are attached to it.
- Normal forceis the force that is exerted by a surface on an object that is in contact with it. The normal force is always perpendicular to the surface.
Force and Equilibrium

Equilibrium is a state of balance in which the net force acting on an object is zero. An object is in equilibrium when the forces acting on it are equal in magnitude and opposite in direction.
There are three conditions that must be met for an object to be in equilibrium:
- The net force acting on the object must be zero.
- The net torque acting on the object must be zero.
- The object must be at rest or moving with constant velocity.
Applications of Force
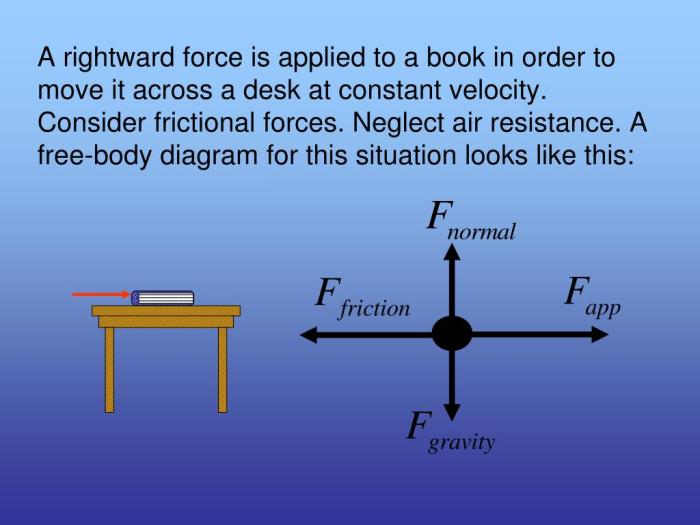
Forces are used in a wide variety of applications, including:
- Engineering: Forces are used to design and build structures, machines, and other objects.
- Construction: Forces are used to move materials, lift heavy objects, and build structures.
- Transportation: Forces are used to propel vehicles and move goods.
Forces can also be used to solve problems and improve efficiency. For example, forces can be used to lift heavy objects, move objects from one place to another, and change the direction of motion of objects.
Measuring and Representing Forces
Forces can be measured using a variety of methods, including:
- Spring scales: Spring scales measure force by measuring the amount of stretch or compression in a spring.
- Force gauges: Force gauges measure force by measuring the amount of deflection in a beam or other object.
- Load cells: Load cells measure force by measuring the amount of strain in a material.
Forces can be represented in diagrams and equations using vectors. A vector is a quantity that has both magnitude and direction. The magnitude of a vector is the length of the vector, and the direction of a vector is the angle between the vector and a reference axis.
FAQ Compilation
What is the relationship between force and motion?
Force is the agent that causes an object to move or change its motion. According to Newton’s second law of motion, the acceleration of an object is directly proportional to the net force acting on it and inversely proportional to its mass.
How does equilibrium relate to forces?
Equilibrium occurs when the net force acting on an object is zero. In this state, the object’s velocity remains constant, and it experiences no acceleration.
What are the different types of forces that can be applied to a dresser?
Various types of forces can act on a dresser, including gravitational force, friction, applied force, and electromagnetic force. Gravitational force pulls the dresser towards the Earth’s center, friction opposes its motion when in contact with surfaces, applied force is exerted by pushing or pulling, and electromagnetic force keeps its components together.