The PDSA cycle forms the conceptual basis for continuous improvement, providing a structured approach to iterative learning and data-driven decision-making. Its four phases—Plan, Do, Study, Act—guide organizations in systematically identifying problems, testing solutions, and implementing sustainable improvements.
Rooted in the scientific method, the PDSA cycle promotes a culture of experimentation and data analysis, enabling organizations to refine their processes and achieve measurable results.
PDSA Cycle Overview
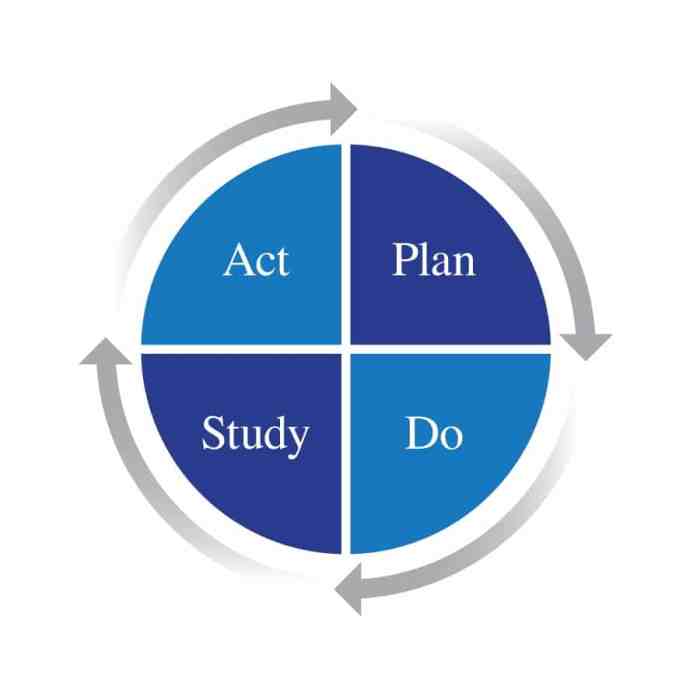
The PDSA (Plan-Do-Study-Act) cycle is a fundamental framework for continuous improvement. It provides a structured and iterative approach to problem-solving, process optimization, and overall performance enhancement.
The cycle consists of four distinct phases:
- Plan:Define the problem, set goals, and develop a plan for improvement.
- Do:Implement the plan and collect data on the results.
- Study:Analyze the data and assess the effectiveness of the improvement.
- Act:Make necessary adjustments based on the analysis and standardize the successful changes.
Conceptual Basis of PDSA
The PDSA cycle is rooted in the scientific method and iterative learning. It promotes a systematic and data-driven approach to improvement by:
- Hypothesis testing:The “Plan” phase involves formulating hypotheses about potential improvements.
- Data collection:The “Do” phase involves collecting data to test the hypotheses.
- Analysis and interpretation:The “Study” phase involves analyzing the data to draw conclusions about the effectiveness of the improvement.
- Iteration:The “Act” phase involves making adjustments based on the analysis and iterating the cycle to further improve the process.
PDSA Cycle in Practice: The Pdsa Cycle Forms The Conceptual Basis For Continuous Improvement
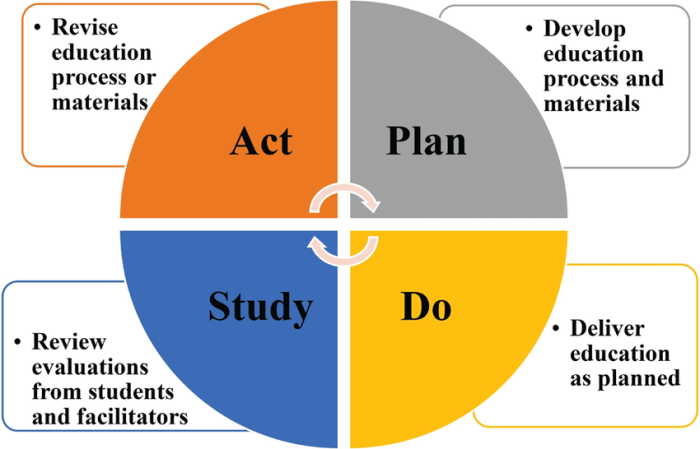
Organizations worldwide have successfully implemented the PDSA cycle to achieve significant improvements in various areas, including:
- Process optimization:Reducing waste and increasing efficiency in production and service delivery.
- Product development:Improving product quality, functionality, and customer satisfaction.
- Service quality:Enhancing customer experiences and reducing complaints.
Challenges associated with implementing the PDSA cycle include:
- Resistance to change:Overcoming resistance from individuals who are comfortable with existing processes.
- Lack of resources:Ensuring adequate time, funding, and personnel for improvement efforts.
- Data collection and analysis:Gathering and interpreting data effectively to inform decision-making.
Integration with Other Improvement Methodologies
The PDSA cycle can be integrated with other improvement methodologies, such as:
- Lean:Focusing on waste reduction and value creation.
- Six Sigma:Emphasizing data-driven decision-making and defect elimination.
- Agile:Iterative and incremental approach to software development.
Combining these approaches leverages their strengths and can lead to more comprehensive and effective improvement initiatives.
Technology and PDSA
Technology plays a crucial role in supporting the implementation of the PDSA cycle by:
- Data collection and analysis:Using sensors, data loggers, and analytics tools to collect and analyze large volumes of data.
- Visualization:Creating dashboards and visualizations to present data in a clear and actionable manner.
- Automation:Automating tasks such as data entry, analysis, and reporting to improve efficiency and reduce errors.
Common Queries
What is the PDSA cycle?
The PDSA cycle is a four-phase iterative process (Plan, Do, Study, Act) used for continuous improvement. It involves planning a change, implementing it, studying the results, and taking action based on the findings.
Why is the PDSA cycle important?
The PDSA cycle provides a structured approach to testing and implementing improvements, reducing the risk of costly mistakes and promoting data-driven decision-making.
How can I use the PDSA cycle in my organization?
Start by identifying a problem or area for improvement. Then, develop a plan to address the issue, implement the plan, study the results, and take action based on your findings.